What Are UTC, UT and GMT
 GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) is a timescale based on the position of the Sun
observed at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London.
UT (Universal Time) is a timescale based on the rotation of the Earth.
UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) is a timescale based on
a caesium atomic clock that synchronised with UT. Today,
UTC is the time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time.
GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) is a timescale based on the position of the Sun
observed at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London.
UT (Universal Time) is a timescale based on the rotation of the Earth.
UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) is a timescale based on
a caesium atomic clock that synchronised with UT. Today,
UTC is the time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time.
What Is Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)?
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London. Before 1 January 1972, GMT was used worldwide as a reference time independent of locations. The meridian at Greenwich is also the Prime Meridian, where longitude is defined to be 0 degree.

Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is calculated roughly like this:
- First, observe each day the actual noon time, which is the moment when the sun reaches its highest point in the sky at Greenwich.
- Then, calculate the annual mean value of the actual noon time. Because of Earth's uneven speed, the mean value may be up to 16 minutes away from the actual noon time on some day.
- Finally, use this mean noon time as the GMT noon time, 12pm GMT, to define the rest of the GMT timescale.
What Is Universal Time (UT)?
Universal Time (UT) is a timescale based on the rotation of the Earth. UT is more accurate than Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). UT is used as the reference time worldwide since 1 January 1972.
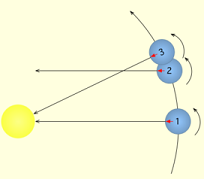
As shown in figure on the right, the rotation of the Earth can be measured based on the Sun or a far away star resulting 2 definitions for the period of day.
- A sidereal day is defined when the Earth has rotated 360 degrees to face the same star again and moved from position 1 to position 2.
- A solar day is defined when the Earth has rotated a little bit more than 360 degrees to face the Sun again and moved from position 1 to position 3.
Universal Time (UT) has several versions:
- UT0 - Universal Time determined by observing the diurnal motion of stars or extragalactic radio sources, and also from ranging observations of the Moon and artificial Earth satellites.
- UT1 - Universal Time computed from observations of distant quasars using long baseline interferometry, laser ranging of the Moon and artificial satellites, as well as the determination of GPS satellite orbits.
- UT1R - A smoothed version of UT1, filtering out periodic variations due to tides.
- UT2 - A smoothed version of UT1, filtering out periodic seasonal variations.
- UT2R - A smoothed version of UT1, incorporating both the seasonal corrections of UT2 and the tidal corrections of UT1R. It is the most smoothed form of Universal Time.
- UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) - An atomic timescale that approximates UT1. It is the international standard on which civil time is based now.
What Is Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)?
UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) is a timescale based on a caesium atomic clock that synchronised with UT. Today, UTC is the time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time.
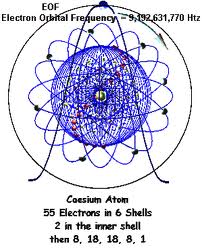
UTC is based on International Atomic Time (TAI) with leap seconds added at irregular intervals to compensate for the Earth's slowing rotation.[2] Leap seconds are used to allow UTC to closely track Universal Time (UT1).
Since the difference between UTC and UT1 is not allowed to exceed 0.9 seconds, if high precision is not required, the general term Universal Time (UT) may be used.[6]
In casual use, when fractions of a second are not important, Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) can be considered equivalent to UTC or UT1. Saying "GMT" often implies either UTC or UT1 when used within informal or casual contexts. In technical contexts, usage of "GMT" is avoided; the unambiguous terminology "UTC" or "UT1" is preferred.[6]
⇒ World Time Zone Information and Tools
✍: Guest
2021-05-21, ∼2023🔥, 0💬